Archive for December 2013
Adobe Photoshop CS6 is a multimedia amp design software related on Adobe Photoshop adobe Photoshop cs6.Follow the Complete video and you will have full version with serial and fully activated version of Photoshop CS6 Extended.Download links are below. Adobe Photoshop CS6 The next generation of Photoshop comes packed with essential new features.Adobe Photoshop CS6 Extended v13.0 Portable by ThumperDC.
{source}
Free Portable Photoshop CS5 65MB Only 100% Working
Posted by Infotechmaestro
Tag :
Downloads,
Photoshop CS5
Portable Photoshop CS5 includes innovative resources to improve the creative
potential of customers. Brand new illustrating resources include a
device Mixing machine Sweep, who blends thousands of shades on one brush
device Bristle Tips, creating the effect of this apply brush. With
Puppet Twist device, customers can change the position or view of any
element of the picture, for example, sorted his curved arm on the images
or modify an picture of the scenery to make a new spatial viewpoint.
{source}
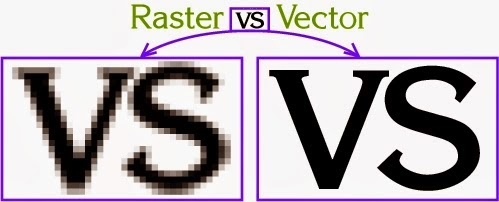
Raster images are made of pixels. A pixel is a single point or the smallest single component in a display device. Let's think of them as little tiny squares* or dots of color or shade.
- Common raster image files: jpg, jpeg, gif, png, tif, tiff, bmp, psd and pdfs originating from raster files
- Common raster programs: paint programs like Photoshop & Paint Shop
- Common raster images: photographs, paintings
Vector images are mathematical calculations from one point to another that form geometrical shapes.
I've magnified the raster and vector images above and we can easily see the differences between the two but sometimes you cannot see the difference at a glance on a normal view. Vector graphics also display an outline or wireframe view and this is very important for certain processes, more details below.
When a raster image is scaled up, it usually loses quality. A raster image can be enlarged by either adding more pixels (which Photoshop randomly - but smartly - adds) or enlarging the size of the pixel. Either way you are spreading the original data over a larger area at the risk of losing clarity.
A vector program will use a mathematical formula to build an image that can be scaled to any size without losing quality.
Raster Images
First let me say: Raster images are also called Bitmap images, pixels are also called dots, and dots-per-inch (dpi) sometimes called pixels-per-inch (ppi) although technically they have distinct meaning I may use those terms interchangeably in this website.
Raster images' dimensions are measured in pixels. Because raster images cannot be enlarged without losing quality, different suppliers have specific size requirements for their processes; they require a specific pixel resolution: a specific amount of pixels within each inch. The amount of pixels within each inch in the image represents the image pixel resolution or ppi (pixels per inch).
When we see an image on a 72 dpi monitor, we are seeing 72 pixels within each inch.
How large a raster image can be printed - and maintain quality - depends on 2 things:
the pixel dimension of the image (e.g. 6824 pixels wide by 2345 pixels high)
the pixel resolution: dots-per-inch (dpi) required by the specific printer
Some offset printers (paper printers) require a minimum of 300 dpi
Some screen printers (t-shirts, cloth) require a minimum of 240 dpi
Large format printers (banners, billboards) vary a lot because it also depends on the distance from which the sign is going to be viewed - could be as low as 20 or more than 200
How to determine what size your raster image must be, for good quality printing:
Multiply the resolution required by the area to be printed. Examples:
If a printer requires a minimum of 300 dpi and you want to print an image in an area that is 5 inches wide, multiply 300 pixels x 5 inches (300 x 5 = 1500). Your image must be at least 1500 pixels wide.
If a printer requires a minimum of 240 dpi and you want to print an image in an area that is 12 inches wide, multiply 240 pixels x 12 inches (240 x 12 = 2880). Your image must be at least 2880 pixels wide.
Can we enlarge the pixel dimension and resolution of a raster image?
Raster images have a certain amount of pixels within each inch. A 72 ppi image has 72 pixels in every inch. A 300 dpi image has 300 dots per inch. Usually the higher the dpi, the higher the quality. When you are required to provide a high resolution image file, the file must have been created or scanned at both the dimension and the resolution required. E.G. if you need to print an image at 2 inches wide and 300 dpi is required, your image must be created/scanned at a minimum of 600 pixels (2in x 300dpi).
Once the image is created at a certain dimension, you may not be able to use this image at a larger size without losing quality. The resolution and size can be manually increased but the quality may suffer. When you manually increase the resolution with a program like Photoshop, Photoshop randomly adds pixels and the result will most likely be a high resolution image of poor quality.
Sample of a raster image below:
When a raster image is scaled up, it usually loses quality. A raster image can be enlarged by either adding more pixels (which Photoshop randomly - but smartly - adds) or enlarging the size of the pixel. Either way you are spreading the original data over a larger area at the risk of losing clarity.
A vector program will use a mathematical formula to build an image that can be scaled to any size without losing quality.
Raster Images
First let me say: Raster images are also called Bitmap images, pixels are also called dots, and dots-per-inch (dpi) sometimes called pixels-per-inch (ppi) although technically they have distinct meaning I may use those terms interchangeably in this website.
Raster images' dimensions are measured in pixels. Because raster images cannot be enlarged without losing quality, different suppliers have specific size requirements for their processes; they require a specific pixel resolution: a specific amount of pixels within each inch. The amount of pixels within each inch in the image represents the image pixel resolution or ppi (pixels per inch).
When we see an image on a 72 dpi monitor, we are seeing 72 pixels within each inch.
How large a raster image can be printed - and maintain quality - depends on 2 things:
the pixel dimension of the image (e.g. 6824 pixels wide by 2345 pixels high)
the pixel resolution: dots-per-inch (dpi) required by the specific printer
Some offset printers (paper printers) require a minimum of 300 dpi
Some screen printers (t-shirts, cloth) require a minimum of 240 dpi
Large format printers (banners, billboards) vary a lot because it also depends on the distance from which the sign is going to be viewed - could be as low as 20 or more than 200
How to determine what size your raster image must be, for good quality printing:
Multiply the resolution required by the area to be printed. Examples:
If a printer requires a minimum of 300 dpi and you want to print an image in an area that is 5 inches wide, multiply 300 pixels x 5 inches (300 x 5 = 1500). Your image must be at least 1500 pixels wide.
If a printer requires a minimum of 240 dpi and you want to print an image in an area that is 12 inches wide, multiply 240 pixels x 12 inches (240 x 12 = 2880). Your image must be at least 2880 pixels wide.
Can we enlarge the pixel dimension and resolution of a raster image?
Raster images have a certain amount of pixels within each inch. A 72 ppi image has 72 pixels in every inch. A 300 dpi image has 300 dots per inch. Usually the higher the dpi, the higher the quality. When you are required to provide a high resolution image file, the file must have been created or scanned at both the dimension and the resolution required. E.G. if you need to print an image at 2 inches wide and 300 dpi is required, your image must be created/scanned at a minimum of 600 pixels (2in x 300dpi).
Once the image is created at a certain dimension, you may not be able to use this image at a larger size without losing quality. The resolution and size can be manually increased but the quality may suffer. When you manually increase the resolution with a program like Photoshop, Photoshop randomly adds pixels and the result will most likely be a high resolution image of poor quality.
Sample of a raster image below:
How to determine what dimension your existing image can be printed at:
- Divide the pixel dimension of your image by the resolution required by your printer.
To view and edit an image pixel dimension you must use a photo-editing program like Adobe Photoshop or Paint Shop Pro to open the raster file.
Examples:
- If your image is 1993 pixels wide & printer requires 300 dpi (1993 ÷ 300) can be printed at 6.643 inches.
- If your image is 1993 pixels wide & printer requires 240 dpi (1993 ÷ 240) can be printed at 8.304 inches.
Tutorials: 15 Steps How to create Photoshop pattern.
Lot of you might be curious on how to define your own cool Photoshop pattern and use it to your own ease. Well don’t be bother because this is very easy and after knowing it you can create thousands of pattern of yours and share it to the community. Now let’s start.
1. Open your Photoshop (I’m using CS5.5 and it works perfectly on CS4 too).
2. Now, open the image you want to create a preset of your pattern. Use the keyboard shortcut “CTRL + O”.
3. Now select Rectangular Marquee tool. Use keyboard shortcut “CTRL + M”.
4. Define the part you will going to use as your pattern. If you want you can select it all
by just using the key shortcut “CTRL + A”.
5. After that, go to Image tab/option.
6. Now find for Define Pattern on the drop down. It must be between Define Brush Preset and Define Custom Shape (depends on PS version).
7. A new small rectangular window will pop out. Now you can name your pattern by just entering your desired one on the Name textbox. Now click Ok button.
8. Now you can close the image and you can now try your pattern.
9. Open up a new workspace. Define what ever name, width and height you want. Use the keyboard shortcut “CTRL + N”.
10. Try to type some words by using the Horizontal Type Tool. Define your own font type. Use the keyboard shortcut “CTRL + T”.
11. Now on the Layer panel, double click your Text layer to open up Layer Style. Or you can right click on it and choose Blending Options.
12. After that, you should be able to see different Styles. Now, browse for the Pattern Overlay, just right between Gradient Overlay and the last style, Stroke (depends on PS version).
13. If the Pattern Overlay is successfully check you can now able to define your own pattern. You can change the default pattern set to your text by just clicking on the inverted triangle on the Pattern box at the middle. You can see different pattern, now you need to choose your pattern you have created.
14. Try playing on it. Better add a Bevel and Emboss and Drop Shadow. Now click on Ok button if it is great for you. Now you can save your cool image to whatever image file type you want.
15. To navigate to your Pattern file, go to this address C:\Program Files\Adobe\Adobe Photoshop CS5.1\Presets\Patterns.
Here's my Fanart for Walter White.. I miss this show so much. I started watching The Walking Dead when it first came out, but began watching Breaking Bad in the beginning of last summer and got hooked. The writing was like no other. The acting and actors were brilliant.now when I watch the Walking Dead, it's like watching a high school play compared to Breaking Bad.
Last week, The Walking Dead Season 4 Episode 6 “Live Bait,” featured the highly-anticipated return of The Governor. The episode attracted 12 million viewers, which was a slight drop from the previous week, but still good enough to be the most-watched cable show of the week.
I love this series! I have NEVER enjoyed and looked forward to any television series as much as I do the Walking Dead Vector.
I'll start form the bottom and work my way up explaining the uses of all the Photoshop tools that I use.
Image Ready - button lets you edit the image in Adobe Image-ready.
Screen Modes - Standard lets you see all the images you're editing in separate windows, the next button maximizes all the windows of the images to the workspace, and the full screen mode maximizes the image to the whole screed over the task-bar.
Foreground and Background Colors - lets you see and change the colors you're editing an image with.
Hand Tool - if you know what it does, tell me.
Zoom Tool - Zoom in a particular part of the image.
Eyedropper - Using Alt you can copy a certain color form an image and draw with that color on the image or a separate image.
Objects Tools - There are Rectangle, Rounded Rectangle, Ellipse, Line, Polygon, and Custom Shape Tools, each of which can be draw on an image.
Text Tools - Let's you put text on an image.
Smudge Tool - Smears the image in the direction you choose.
Blur Tool - Blurs an image in areas you select.
Paint Bucket Tool - Fills a chosen color on to an image with the selected color.
Erase Tool - Erases an image to its background, either white, a selected color, or transparent.
Clone Stamp Tool - Using Alt you can select a part of an image and recopy that part to a different image or to a different area of the same image.
Brush Tool - Draws lines of a selected brush in a direction you choose.
Pencil Tool - Draws lines of a selected brush in a direction you choose, without anti-aliasing.
Crop Tool - Crops the image to the area selected.
Move Tool - Moves the objects or layers in the image, or the image itself.
Wand Tool - Selects a color and its shades so that only that part of an image can be modified or added effects to.
Lasso Tool - Lets you select a part of an image to be modified by itself.
Marquee Tools - Let's you select a defined object of an image or creat a defined object.
Photoshop Tools lets you create your own workspace that fits you the best.
You can move or get rid of any options and settings windows in your workspace so that it can be used to your best interest.
Adobe Photoshop is an image editing, or image creating application, with a lot of advanced and useful tools.
Photoshop Definitions and Terms:
- Image - picture, a visual representation of an object or scene or person or abstraction produced on a surface.
- Pixel - the information stored for a single grid point in the image. The complete image is a rectangular array of pixels. A pixel consists of a single color.
Difference between Canvas Size and Image Size
The image is an object that was drawn and when changing the size of it, it either shrinks or expands, canvas is the space provided to draw the image on, decreasing the size of the canvas doesn't shrink the image but cuts it off, when increasing the canvas size there is more space provided and you can draw out side of the image.
The image is an object that was drawn and when changing the size of it, it either shrinks or expands, canvas is the space provided to draw the image on, decreasing the size of the canvas doesn't shrink the image but cuts it off, when increasing the canvas size there is more space provided and you can draw out side of the image.
- Transparent - if an image is not transparent, the image is automatically a rectangular size, if the image is transparent, for instance a circle will always be a circle, the canvas is transparent so the pixels around the circle are non existent.
- Anti-aliasing - Smoothing or blending the transition of pixels in an image. Anti-aliasing the edges on a graphic image makes the edges appear smooth, not jagged.
- Layer - layers pile on top of each other, think of it as earth's layers of soil, crust and so on. You can change th order of layers, depending if you want an image under an image or the other way around.
- Filter - under Filter you will find numerous effects you can apply to a image or selected region of an image.
- Bitmap - A representation, consisting of rows and columns of dots, of a graphics image in computer memory. The value of each dot (whether it is filled in or not) is stored in one or more bits of data.
- Gray scale - An image representation in which each pixel is represented by a single sample value representing overall luminance (on a scale from black to white).
- RGB Color - The red, green, and blue (RGB) color system can represent a large portion of the color spectrum by mixing these three primary colors.
- Lab Color - a color model developed by the Center Internationale d´Eclair-age (CIE). These standards are internationally accepted standards for all colorimetric measurements. The Lab model, like other CIE color models, defines color values mathematically, in a device independent manner. Lab color is consistent color regardless of the device producing the color.
Technically, it’s the words "vector" and "pixel" combination. That’s why when you say “Can you vector my photo in Photoshop?” That’s just wrong.
The difference between Vector and Vexel graphics is this:
The difference between Vector and Vexel graphics is this:
- Vector graphics is done usually in Adobe Illustrator.
- Vexel graphics is done in Adobe Photoshop.
When you zoom in a vector image, the image is not pixelated. When you zoom in a vexel image, the image is pixilated. But when you zoom out both, they are almost the same.
Here are the VXY abbreviations and meanings.
VXY Groups abbreviations:
- AI [ Adobe Illustrator ]
- A/W [ Artwork ]
- Az [ Abduzeedo ]
- CnC [ Comment & Critism (Critique) ]
- DA [ Deviantart (deviantart.com) ]
- DF [ Daily Feature (Shadowness) ]
- DI [ Daily Inspiration (Shadowness) ]
- DP [ Digital Painting ]
- Desgr [ Designer ]
- EB [ Eyeball ]
- FTW [ For the Win ]
- GEB [ Grand Eyeball ]
- PMS [ Pantone Matching System ]
- SN [ Shadowness (shadowness.com) ]
- Tradi [ Traditional ]
- OT [ Off Topic ]
- PS [ Photoshop ]
- VxV [ Vector X Vexel ]
- WIP [ Work In Progress ]
Fake Vector
Vectors are made using specific software's such as Illustrator (most used professionally), CorelDRAW (pretty easy to learn) or Ink scape (free software). The Photoshop works with raster images (bitmaps, that ones formed by pixels). When we finish our work we’ll save that as a bitmap (.jpg, .tif, .pgn, .gif). So that, we say that it’s a fake vector.
Take a look at this image i just made it in 10 seconds a sample fake Vector
Just because something is "cell shaded" or "flat colored" does not make it a Vector. The use of filters (cutout, etc.) creates a raster-based image and thus is disqualified from ever being considered a vector image. Only a vector program such as the ones mentioned above can create a vector image.
A vector takes time to create. The artist makes decisions on how much or how little detail to include. The artist makes decisions on colors to use. These are the same decisions one makes before sitting down with conte crayons, pastels or oil paint.
I understand that these days there is some program overlap. Photoshop has some vector tools and Illustrator has some raster tools, but if you use the lasso and the paint bucket, you are not creating vector-based artwork. If you run a filter you are not creating vector-based artwork.
The image quality in vector-based graphics does not depend on the DPI of the output device. This type of artwork in graphic design is good for logo designs because the resulting image is clear and crisp. Vector-based graphics do not work well when there is a need for soft-toned graphics in a picture. A picture which requires a lot of tonal changes is difficult to achieve in vector art. If you are interested in adding a vector-based image on your web page then you need to rasterize the image (convert it into a bitmap image). But the vector images that are created in Flash can be used in a web page without converting it. Besides Flash, there are several plug-ins that are available which support vector-based images. In many cases, the browsing software faces trouble in dealing with a vector-based graphics and rasterizes the vector image itself.
Vector-based images cannot be for realistic pictures. This is very important to know that the conversion of pixel-based image into a vector-based image is very difficult. It can only be done by using specific software. It is wise to use bitmap images in graphics or for web design because images produced by scanners and digital devices are bitmap images and the conversion of pixel-based image into a vector image is a difficult task.
How to Use Pen Tool
In this Photoshop tutorial we will explore how to use the pen tool.
First, we will look at the pen tool’s basic controls. We will examine creating paths, curvature modification and anchor point adjustments.
Next, on the following page, we will use our new pen tool skills to cut out an image. This skill is so essential to know when using Adobe Photoshop, and it really illustrates the power behind the pen tool.
Finally we will see how a path created with the pen tool can be used to create custom shapes. Custom shapes are vectors so they will never pix-elate or lose quality. Again this is such a handy skill, you’ll end up using it all the time!
BASIC CONTROLS OF THE PEN TOOL
- Photoshop’s pen tool you have three options: Create a new work path, Create a new shape layer, and Fill Pixels.
- We will use the Create a new work path option as this the most commonly used. You can find these options in the top left hand corner of the Photoshop window. See the image below.
- Just like selection tools, the pen tool has several different options for the resulting path. The most commonly used is “add to path area”. See image below.
- Take your pen tool and click on a blank canvas similar to what I have done below. Each time you click you create an anchor point.
- Hold down Shift, move the mouse and click again. Holding down shift while making an anchor point creates it in a straight line with the last anchor point.
- We can add and delete anchor points on the path we have created. Right click on the pen tool on the toolbar to reveal further tools. Use the Add and Delete Anchor Point Tool to do just that!
- I used the Delete Anchor Point Tool to remove the forth anchor point.
- Now, let’s look at the Convert Point Tool for curvature modification and moving anchor points.
- With the convert point tool click and drag on the second anchor point. Without letting go, move the mouse around and see how it affects the curve. The line that is created is called the Tangent Line. The tangent line controls the curvature of the curve.
- Holding down Ctrl click on the anchor point and move the mouse, see how this allows you to move the anchor point.
- Click on one end of the tangent line and drag.
- This breaks the tangent line in half and creates sharp path changes.
- Move the entire path by selecting the Path Component Selection Tool from the toolbar and drag the path to a new location.
- Delete your path by right clicking on the path and select Delete Path.
Finally I will briefly touch on another style of creating a path. With your pen tool create two anchor points however on the second click don’t let go, drag the click to create the tangent line. The tangent line will affect the next anchor point that you create. Try it out. I don’t use this technique because I find it slower but many do use the technique that feels right for you. Thanks for reading the Basics Photoshop Pen Tool.
Vector art is define as a very popular type of graphic design. Created with the aid of a computer, vectors are a collection of shapes, curves, and colors that create an overall image. Unlike other types of graphic art, vector art can be infinitely scaled without losing its quality. The same quality ratio is the same whether an image is at 1024 x 768 pixels or the size of a billboard. Vector programs are often used to create a cartoon-like effect, but some artists push the boundaries to create impressively realistic art.
If you're new to vectoring, it will definitely be easier to use a base image. Because most vector graphics editors utilize layers, you can add this base image to the bottom layer and trace over the image. Be sure to lock the reference layer so that you do not inadvertently alter it.
When choosing an reference image to vector, it is best to use images with higher resolutions. The bigger the image, the easier it is to see and vector the details. Look for images that are in color and avoid sepia or black and white. Although vectors can use black and white reference images, it's easier to work with colors initially. Colors help to define lines and create subtle shadow.
The key to a great vector is preparation. It is very difficult to create a precise vector without an outline. Create a new layer on top of the reference image. Depending on your graphics editor, you will use either a pen tool or a line tool to create an outline of your image. Both the pen and line tools create precise shapes. The outcome of this process is known as line art. It will look similar to images in coloring books.
To create an outline, select one point on your image. Drag the pen or line tool to the next point in your image. Alter the line to match the curve of your reference image. Use a color in sharp contrast to the reference image, in order to see the line better as you draw.
Coloring in the line art can be both exciting and tedious.
Depending on the style of your vector, you will need to either fill color inside the lines you've just created, or you will paint colors onto the vector on separate layers. The most popular form of coloring is to fill the lines with solid or gradient colors. You may find yourself working with various transparency levels to create the right depth of color for your image. If you're not already, become very acquainted with your "undo" button.
For the most realistic coloring, take the eyedropper and sample off of your reference image. You'll do that by clicking on various spots on your reference image, and making note of the 6 digit color number. Use that color number as your paint bucket fill.
If you prefer to have your image in black and white, use an image editor like Photoshop to desaturated the color. By colorizing a vector and then desaturating it, you will ensure a more realistic black and white image. Be care to save your work as an .eps file after working in Photoshop to keep your image a vector.
This Vector Human Eye Shading Video Tutorial gives you a full tips and tricks on how to do a vector eye shading.on your own Photoshop computer.
Video tutorial: {source}
Things you need:
The pen tool
In order to create vector art, you must first master the pen tool. This comprehensive guide aims to introduce you to features, shortcuts, and methods for working with what is arguably Adobe's most essential tool.
In order to create vector art, you must first master the pen tool. This comprehensive guide aims to introduce you to features, shortcuts, and methods for working with what is arguably Adobe's most essential tool.
Drawing vector graphics
This video tutorial is a really useful resource for explaining exactly how to create vector art in Illustrator.
Creating simple, organic shapes
Learn how to create simple, organic vector shapes in Illustrator with this easy-to-follow tutorial from graphic and web designer Veerle Pieters.
Add texture to your vector illustrations
Adding texture to your vector art is a great way to give it more dimension and perspective. In this easy to follow video, Illustrator expert Alexandra Cecilio explains how to get the most out of textures.
Adding texture to your vector art is a great way to give it more dimension and perspective. In this easy to follow video, Illustrator expert Alexandra Cecilio explains how to get the most out of textures.
Learn how to create a simple vector eye! This helpful infographic tutorial shows the process of creating an eye with minimal shading. One of our different ways of vectoring eyes tutorial. Just control the opacity in shading. You can make anything style you want. In the white eye part, just don't use pure white color. I always use Gray or lighter gray. Just experiment the colors and color blending. This was done in Adobe photoshop cs5.
{source}
It's hard to tell the difference between a created vexel and a vector. This is because they are not a style of art, but a medium of art.
When we say a "medium" we mean with how a piece of art is created or what with. For instance we have both traditional and digital paintings. A traditional painting is created with, for example, oils and water colours. however a digital painting is created with, for example, you use a paint brush tool or smudge/dodge/burn tool. Although the end result is the same, it's what it's been made with which is the key difference... and especially how we categorize it on deviantART.
Vexel art: created using raster layers.
Vector art: created using vector layers.
It's easy to remember vectors are made with vector layers... but to associate vexels with raster layers is a little less easy.
The word "vexel" was created based on work appearing to be vector art, but was on raster layers which consist of pixels.
Ok, this is a little exercise you can do to show you the difference.
1) Right click on your own avatar and save it to your desktop.
2) Open it in your graphics program of choice.
3) Zoom into the image as much as you can... well maybe until about 500%
Below is the example avatar zoomed in at 500%:
Looking at your avatar you can see how it is made up of coloured squares. These squares are pixels and show that your .jpg/.gif or .png file of this image is on a raster layer.
1) Now zoom back to 100%
2) Go to Edit > Resize or Image > Resize --- or which ever way to resize the image size.
3) Increase the size to say 500% of the original size
Below is the example avatar resized in at 500%:
Depending on the program you have used, you will either see the coloured squares... or you may see a big version of your avatar but with blurred lines and not as sharp as your original sized avatar.
In the first image, your art program read the file and the file told it that for each single pixel in your avatar, it wants it to be a specific colour and in a certain place.
When you resize it, your art program tries to do the best it look as smooth as possible when the size is increased... and to not make the image look pixelated.
Vector
"Vector is a digital art that is an entirely pixel-based form of raster art that
imitates the vector graphics technique, but is distinguished from
normal vector graphics or raster images."
Vexel
Vexel is a neologism for an entirely pixel-based form of raster art that imitates the visual appearance of vector graphics technique (i.e. sharp-edged lines and areas of flat colour or smooth gradient fills).by:{ wikepedia }
"Vexel itself is a mixture of two words ‘Vector’ and ‘Pixel’. Vexel
designs are composed by using multiple layered shapes. It can be done in
Photoshop, but vexel designs are not limited to only Photoshop;
essentially, it can be done with any image editing software that has a
good Pen Tool."